CLIMATE SECURITY & WATER STRESS
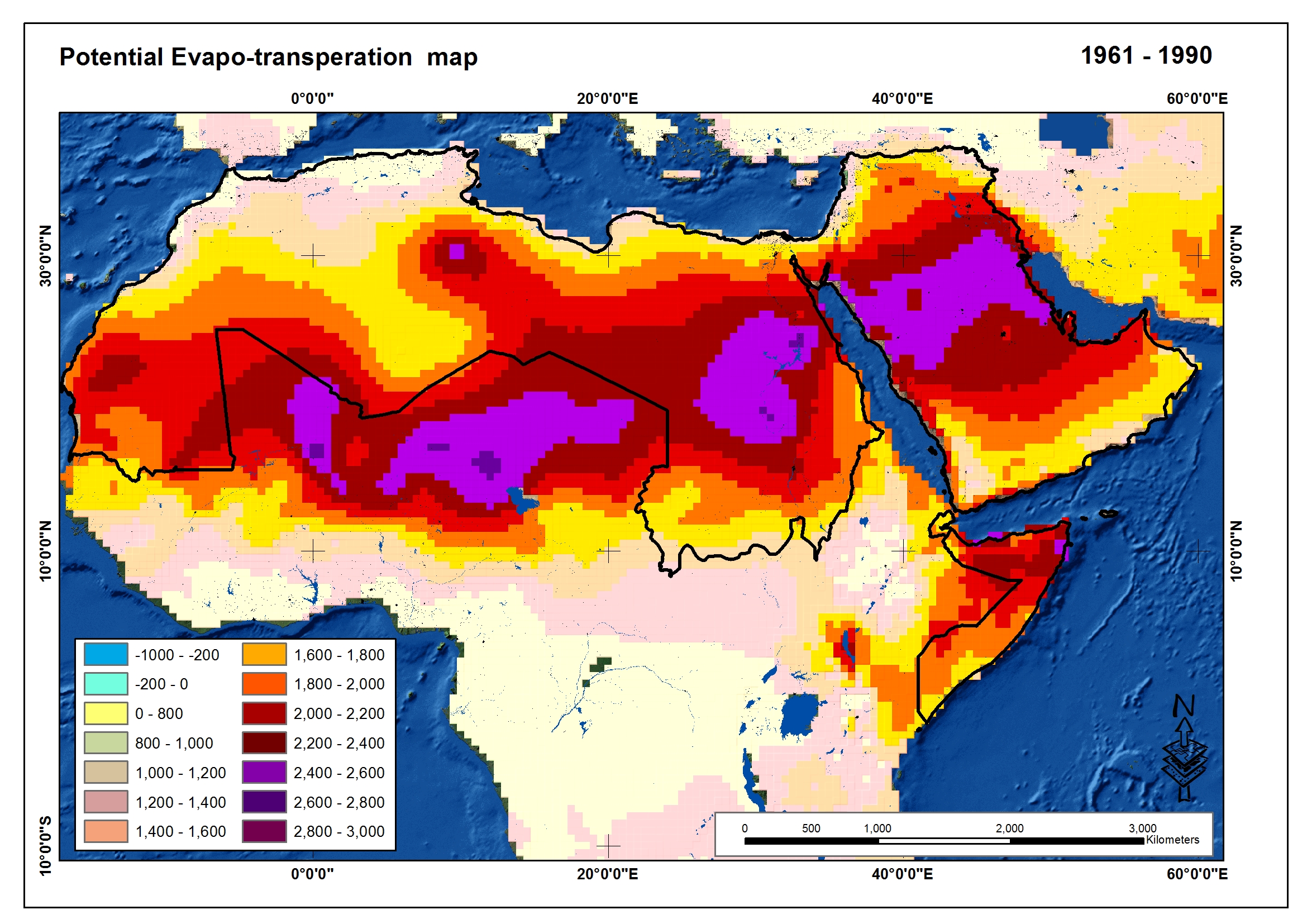
Climate security is causing additional water stress in a region that is already extremely affected by water scarcity. The arid to semi-arid climate, the lack of renewable water resources that lie within the boundaries of the Arab countries...
READ MORE
CLIMATE SECURITY & FOOD SECURITY
The Arab world has the highest food deficit and is the highest food-importing region globally. The average annual increase in the food production and consumption gap is increasing throughout the past few years...
READ MORE
CLIMATE SECURITY & ENERGY SECURITY
Our energy systems, including industry and transportation systems, rely by around 80% on the use of fossil fuels. The combustion of fossil fuels releases CO2 and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere...
READ MORE
CLIMATE SECURITY, SOCIAL COHESION & GENDER EQUITY
imate change phenomena, such as rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns and rainfalls, sea level rise, and the increase in extreme and destructive weather, have an immediate impact on social security and wellbeing...
READ MORE